5-Amino-1MQ: The Complete Guide to the NNMT Inhibitor
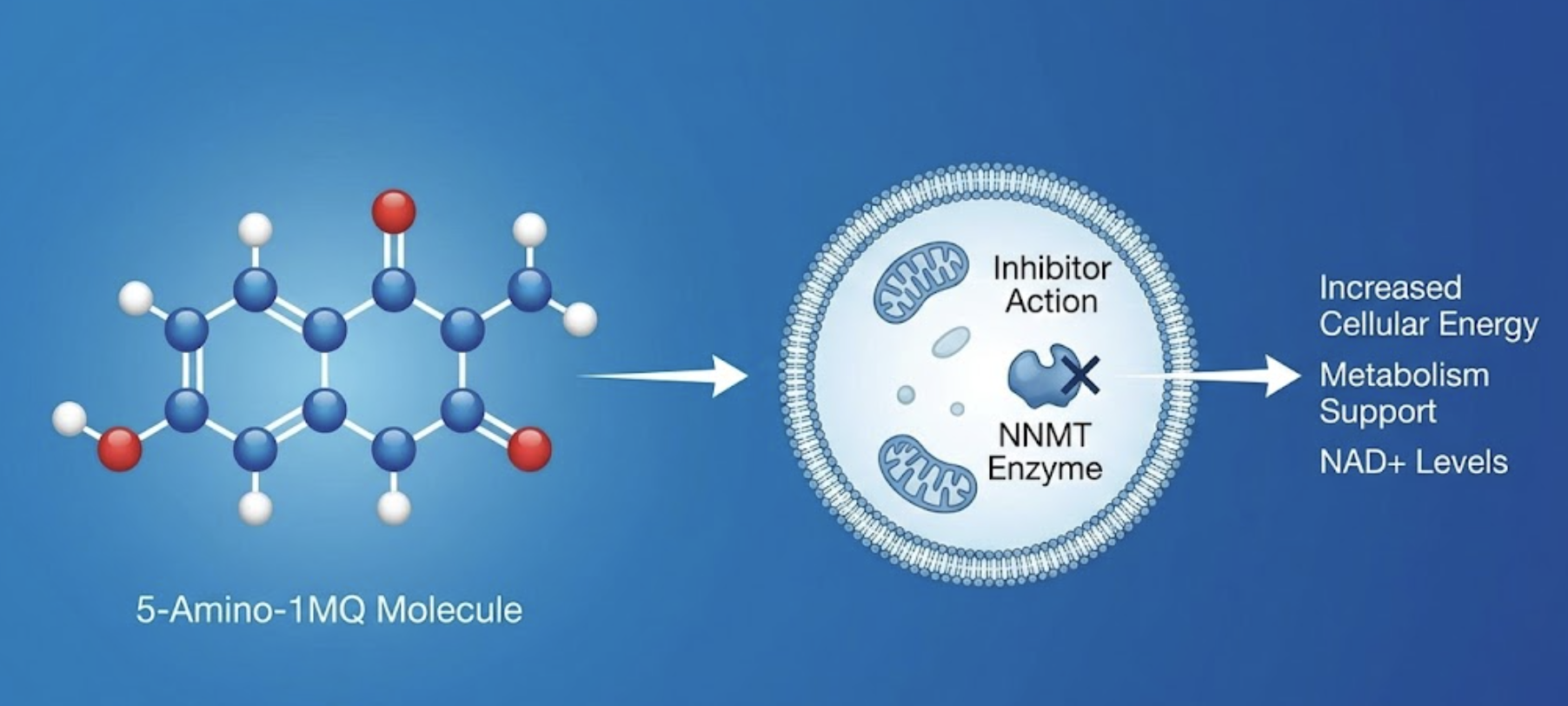
5-Amino-1MQ (5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium) is emerging as one of the most exciting compounds in metabolic research. Unlike traditional weight loss peptides that suppress appetite or mimic hormones, 5-Amino-1MQ works through a completely different mechanism.
Introduction
5-Amino-1MQ (5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium) is emerging as one of the most exciting compounds in metabolic research. Unlike traditional weight loss peptides that suppress appetite or mimic hormones, 5-Amino-1MQ works through a completely different mechanism—inhibiting the enzyme NNMT (nicotinamide N-methyltransferase) to fundamentally shift how your body processes and stores fat.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about 5-Amino-1MQ: what it is, how NNMT inhibition works, the research behind its fat loss and metabolic benefits, dosing protocols, potential side effects, and how it compares to other weight loss compounds like semaglutide and AOD-9604.
Important Disclaimer: 5-Amino-1MQ is not FDA-approved for human use and remains a research compound. No human clinical trials have been published as of 2025. This article is for educational purposes only. Always consult with a healthcare provider before considering any experimental compounds.
Table of Contents
- What is 5-Amino-1MQ?
- Understanding NNMT: The Key Enzyme
- How 5-Amino-1MQ Works
- Research & Scientific Evidence
- Benefits of 5-Amino-1MQ
- Dosage Guidelines
- Side Effects & Safety
- 5-Amino-1MQ vs Other Fat Loss Compounds
- Stacking 5-Amino-1MQ
- Who Should Consider 5-Amino-1MQ
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Scientific References
What is 5-Amino-1MQ?
Definition & Overview
5-Amino-1MQ (5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium) is a small-molecule compound classified as a selective NNMT inhibitor. It's technically not a peptide (peptides are chains of amino acids), but it's often discussed in peptide therapy contexts due to its use in similar applications—particularly metabolic optimization and fat loss.
Key Characteristics:
| Property | Specification |
|---|---|
| Full Name | 5-Amino-1-methylquinolinium |
| Abbreviation | 5-Amino-1MQ |
| Class | Small molecule NNMT inhibitor |
| Molecular Weight | ~159 Da |
| Administration | Oral (capsule) |
| Half-Life | Estimated 12-16 hours |
| Primary Target | NNMT enzyme |
| FDA Status | Not approved (research compound) |
What Makes 5-Amino-1MQ Unique?
Unlike most fat loss compounds that work through:
- Appetite suppression (GLP-1 agonists like semaglutide)
- Growth hormone pathways (HGH, AOD-9604)
- Thermogenesis (stimulants)
- Thyroid modulation (T3/T4)
5-Amino-1MQ takes a fundamentally different approach by targeting cellular metabolism directly. It blocks an enzyme (NNMT) that when overactive, promotes fat storage and reduces energy expenditure. By inhibiting this enzyme, 5-Amino-1MQ shifts the body toward burning fat rather than storing it—without suppressing appetite or significantly affecting hormones.
The Discovery of 5-Amino-1MQ
5-Amino-1MQ emerged from research into NNMT, an enzyme discovered to be significantly overexpressed in obese individuals and those with metabolic dysfunction. Scientists at the University of Texas identified that blocking NNMT could reverse obesity in animal models, leading to the development of selective NNMT inhibitors like 5-Amino-1MQ.
The compound gained attention after a landmark 2018 study published in Biochemical Pharmacology demonstrated that NNMT inhibitors could reverse diet-induced obesity in mice without affecting food intake—a remarkable finding suggesting true metabolic enhancement rather than simply eating less.
Understanding NNMT: The Key Enzyme
To understand how 5-Amino-1MQ works, you need to understand NNMT (Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase)—the enzyme it targets.
What is NNMT?
NNMT is a cytosolic enzyme that methylates nicotinamide (vitamin B3/niacin) using SAM (S-adenosylmethionine) as a methyl donor. This produces 1-methylnicotinamide (MNA).
Why This Matters:
- Nicotinamide is a precursor to NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
- NAD+ is essential for hundreds of metabolic reactions, including energy production
- When NNMT is overactive, it depletes nicotinamide, reducing NAD+ production
- Lower NAD+ = impaired metabolism, reduced fat burning, accelerated aging
NNMT and Obesity
Research has established a clear connection between NNMT and metabolic dysfunction:
Key Findings:
NNMT is overexpressed in obesity: Studies show NNMT levels are significantly elevated in white adipose tissue (fat) and liver of obese individuals
Genetic link: Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the NNMT gene are associated with obesity, type 2 diabetes, hyperlipidemia, and metabolic syndrome
NNMT knockdown reverses obesity: Mice genetically engineered to lack NNMT are resistant to diet-induced obesity and show improved insulin sensitivity
Adipose tissue focus: NNMT expression is particularly high in white adipose tissue, making it a direct target for fat reduction
The NNMT-NAD+-SIRT1 Pathway
Here's the simplified pathway that explains 5-Amino-1MQ's effects:
HIGH NNMT Activity (Problem State):
Nicotinamide → (NNMT consumes it) → 1-MNA
Result: Less NAD+ → Lower SIRT1 activity → Fat storage, reduced metabolism
LOW NNMT Activity (With 5-Amino-1MQ):
Nicotinamide → (NNMT blocked) → Available for NAD+ synthesis
Result: More NAD+ → Higher SIRT1 activity → Fat burning, enhanced metabolism
SIRT1: The Longevity Gene
When NAD+ levels increase (due to NNMT inhibition), it activates SIRT1 (Sirtuin-1), often called the "longevity gene." SIRT1 activation leads to:
- Increased fat oxidation (burning fat for energy)
- Improved mitochondrial function
- Enhanced insulin sensitivity
- Reduced inflammation
- Cellular repair and autophagy
- Potential lifespan extension (demonstrated in animal models)
This is why 5-Amino-1MQ is discussed not just for fat loss but also in anti-aging contexts.
How 5-Amino-1MQ Works
Primary Mechanism: NNMT Inhibition
5-Amino-1MQ is a selective and membrane-permeable NNMT inhibitor. It enters cells and binds to the NNMT enzyme, preventing it from methylating nicotinamide.
Selectivity is Key:
5-Amino-1MQ specifically targets NNMT without inhibiting related methyltransferases or enzymes in the NAD+ salvage pathway. This selectivity is important for minimizing off-target effects.
Downstream Effects
When NNMT is inhibited by 5-Amino-1MQ:
1. NAD+ Levels Increase
- More nicotinamide available for NAD+ biosynthesis
- NAD+ is the critical coenzyme for energy metabolism
- Higher NAD+ improves mitochondrial function
2. SIRT1 Activation
- NAD+ activates SIRT1 (NAD+-dependent deacetylase)
- SIRT1 regulates genes involved in fat metabolism
- Promotes oxidation of fatty acids over storage
3. Reduced Lipogenesis
- Decreased creation of new fat cells (adipogenesis)
- Reduced conversion of calories to stored fat
- Smaller adipocyte (fat cell) size
4. Increased Energy Expenditure
- Higher basal metabolic rate (BMR)
- More calories burned at rest
- Enhanced thermogenesis
5. Improved Metabolic Markers
- Better insulin sensitivity
- Improved glucose tolerance
- Lower cholesterol levels
What 5-Amino-1MQ Does NOT Do
Understanding what 5-Amino-1MQ doesn't do is equally important:
- ❌ Does NOT suppress appetite (unlike GLP-1 agonists)
- ❌ Does NOT affect testosterone or cortisol (unlike some fat burners)
- ❌ Does NOT significantly affect thyroid function
- ❌ Does NOT stimulate the CNS (no stimulant effects)
- ❌ Does NOT cause muscle loss (may actually preserve muscle)
This makes 5-Amino-1MQ attractive for those who want to avoid the side effects of appetite suppressants (nausea, food aversion) or stimulants (anxiety, sleep disruption).
Research & Scientific Evidence
The Landmark Study (2018)
The most significant research on NNMT inhibitors, including 5-Amino-1MQ, was published in Biochemical Pharmacology (2018) by Neelakantan et al.
Study Design:
- Diet-induced obese (DIO) mice
- Treatment with 5-Amino-1MQ and related NNMT inhibitors
- Measured: body weight, fat mass, adipocyte size, metabolic markers
Key Results:
| Outcome | Result |
|---|---|
| Body Weight | ~5% reduction in 10 days |
| White Adipose Mass | ~35% decrease |
| Adipocyte Size | Significantly reduced |
| Food Intake | No change (not appetite-related) |
| Adverse Effects | None observed |
Critical Finding:
"5-amino-1MQ-treated mice had significantly reduced body weights, white adipose masses, and adipocyte sizes... Notably, 5-amino-1MQ treatment did not show a significant impact on the food intake and any observable adverse effects."
This is remarkable because it demonstrates metabolic fat loss without appetite suppression—the body simply became more efficient at burning fat.
Cellular Studies
In Vitro (Cell Culture) Findings:
- 5-Amino-1MQ significantly reduced intracellular MNA (the product of NNMT)
- Increased intracellular NAD+ levels
- Suppressed lipogenesis (fat creation) in adipocytes
- Did not inhibit related enzymes (high selectivity)
Combined Treatment Research (2022)
A follow-up study published in Scientific Reports examined combining NNMT inhibition with calorie restriction:
Finding:
"Treatment with 5-amino-1-methylquinolinium combined with low-fat diet promoted dramatic whole-body adiposity and weight loss in diet-induced obese mice, rapidly normalizing these measures to age-matched lean animals."
This suggests 5-Amino-1MQ may work synergistically with dietary interventions.
Microbiome Effects
The same 2022 study revealed an interesting finding: NNMT inhibition combined with diet changes altered the gut microbiome in ways associated with leanness:
"Reduced calorie diet combined with NNMT inhibition establishes a distinct microbiome in DIO mice."
This opens questions about whether 5-Amino-1MQ's benefits extend to gut health and metabolic signaling.
Limitations of Current Research
Important Caveats:
- No published human clinical trials as of 2025
- All significant research is in animal models (mice)
- Long-term safety in humans is unknown
- Optimal human dosing has not been established through clinical trials
- Mechanism is well-understood, but human translation needs confirmation
Benefits of 5-Amino-1MQ
Based on preclinical research and anecdotal reports from clinical practitioners, 5-Amino-1MQ offers several potential benefits:
1. Fat Loss & Body Composition
Primary Benefit: Targeted Fat Reduction
- Reduces white adipose tissue (stored fat)
- Decreases adipocyte (fat cell) size
- Targets visceral fat (the dangerous belly fat around organs)
- Promotes fat burning without muscle loss
Mechanism: By increasing NAD+ and activating SIRT1, the body shifts from fat storage mode to fat oxidation mode.
What Users Report:
- Noticeable reduction in waist circumference
- Reduction in "stubborn fat" areas
- Improved body composition (lower body fat percentage)
- Results often seen within 4-6 weeks
2. Metabolic Enhancement
Increased Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
- Burn more calories at rest
- Enhanced cellular energy production
- Improved mitochondrial function
Better Metabolic Flexibility:
- Improved ability to switch between fuel sources
- Better utilization of fat for energy
- Enhanced insulin sensitivity
3. Muscle Preservation
Unlike many weight loss interventions that cause muscle loss along with fat loss, 5-Amino-1MQ appears to preferentially target fat while preserving lean mass.
Why This Matters:
- Muscle loss reduces BMR, making future weight gain easier
- Preserving muscle maintains strength and function
- Better body composition outcomes
4. Energy & Cognitive Benefits
Many users report subjective improvements in:
- Mental clarity and focus
- Sustained energy levels (without stimulant jitters)
- Reduced fatigue
- Improved motivation
Potential Mechanism: Enhanced NAD+ supports mitochondrial function in the brain as well as muscles, potentially improving neuronal energy metabolism.
5. Anti-Aging Potential
Through NAD+ enhancement and SIRT1 activation:
- Improved cellular repair mechanisms
- Enhanced autophagy (cellular cleanup)
- Better mitochondrial health
- Potential longevity benefits (demonstrated in animal models)
5-Amino-1MQ is increasingly discussed in longevity and anti-aging circles due to these NAD+-related effects.
6. Metabolic Health Markers
Research suggests improvements in:
- Insulin sensitivity
- Fasting blood glucose
- Cholesterol levels (particularly total cholesterol)
- Inflammatory markers
Summary of Benefits
| Benefit | Evidence Level | User Reports |
|---|---|---|
| Fat Loss | Strong (animal studies) | Consistently positive |
| Metabolic Rate Increase | Strong (animal studies) | Positive |
| Muscle Preservation | Moderate | Positive |
| Energy/Focus | Anecdotal | Commonly reported |
| Insulin Sensitivity | Strong (animal studies) | Positive |
| Anti-Aging | Theoretical/Emerging | Early reports positive |
Dosage Guidelines
Standard Dosing Protocol
While optimal human dosing hasn't been established through clinical trials, the following represents commonly used protocols in clinical practice:
Typical Dosage:
| Protocol | Dosage | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | 50 mg | 3x daily with meals |
| Conservative | 50 mg | 2x daily |
| Higher | 100 mg | 2x daily |
| Maximum | 150 mg | Total daily dose |
Administration:
- Taken orally (capsule form)
- Best taken with meals
- Some practitioners recommend spacing doses throughout the day
Cycling Protocol
Important: Unlike some compounds that can be taken continuously, 5-Amino-1MQ appears to work best when cycled.
Recommended Cycle:
| Phase | Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| On Cycle | 6-8 weeks | Active supplementation |
| Off Cycle | 2-4 weeks | Break period |
| Repeat | As needed | Monitor response |
Why Cycling?
- Effects may diminish after 4-6 weeks of continuous use
- Allows metabolic systems to reset
- May improve long-term effectiveness
- Follows patterns used for other NNMT-targeting approaches
Factors Affecting Dosage
Consider adjusting dosage based on:
- Body weight: Higher body weight may benefit from higher doses
- Response: Some individuals respond better to lower or higher doses
- Goals: More aggressive fat loss may warrant higher end of range
- Side effects: Reduce if side effects occur
- Stacking: May need lower dose when combined with other compounds
Important Dosing Notes
- Start conservatively: Begin with lower doses to assess tolerance
- Take with food: May reduce any GI discomfort
- Stay hydrated: Adequate water intake supports metabolism
- Monitor response: Track body composition, not just weight
- Consult a professional: Work with a knowledgeable healthcare provider
Side Effects & Safety
Reported Side Effects
Based on preclinical research and clinical practitioner reports, 5-Amino-1MQ appears to be well-tolerated. Reported side effects are generally mild and transient:
Common (Mild):
- Nausea (usually temporary)
- Mild GI upset
- Headache
- Drowsiness or fatigue (in some users)
- Changes in appetite (typically minor)
Less Common:
- Sleep disturbances (reported by some practitioners)
- Dizziness
- Temporary changes in energy levels
Safety Profile from Research
Animal Studies:
"Mice tolerated it very well with no observable adverse effects even at high doses, and doses up to 60 mg/kg per day produced no signs of toxicity in preclinical testing."
The animal research suggests a favorable safety profile, but this doesn't guarantee the same in humans.
Important Safety Considerations
Unknown Factors:
- No published human clinical trials
- Long-term effects unknown
- Interactions with medications not studied
- Effects in special populations not established
Contraindications (Theoretical/Precautionary):
| Condition | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Pregnancy | Avoid |
| Breastfeeding | Avoid |
| Kidney disease | Avoid or use with caution |
| Liver disease | Avoid or use with caution |
| Active cancer | Consult oncologist (NAD+/growth concerns) |
| Under 18 | Avoid |
Comparison with Other Compounds
| Safety Aspect | 5-Amino-1MQ | Semaglutide | Stimulants |
|---|---|---|---|
| GI Side Effects | Mild/rare | Very common | Variable |
| Cardiovascular | Not observed | Some concerns | Significant |
| Hormonal Disruption | Not observed | Minimal | Variable |
| Sleep Disruption | Rare | Not typical | Common |
| Dependency Risk | Not observed | Not typical | Present |
Recommendations for Safe Use
- Medical supervision: Work with a healthcare provider knowledgeable about peptides/research compounds
- Blood work: Monitor metabolic markers before and during use
- Start low: Begin with conservative doses
- Quality source: Use reputable suppliers with third-party testing
- Monitor for changes: Note any unusual symptoms
- Cycle appropriately: Don't use continuously without breaks
- Stop if needed: Discontinue if significant side effects occur
5-Amino-1MQ vs Other Fat Loss Compounds
5-Amino-1MQ vs Semaglutide (Ozempic/Wegovy)
| Aspect | 5-Amino-1MQ | Semaglutide |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | NNMT inhibition → NAD+ increase | GLP-1 receptor agonist |
| Primary Effect | Metabolic enhancement | Appetite suppression |
| FDA Approved | No | Yes |
| Administration | Oral (capsule) | Injection (weekly) |
| Appetite Effect | Minimal/none | Strong suppression |
| Nausea | Rare | Very common |
| Weight Loss | Moderate (5-7% in animals) | Strong (10-15% in humans) |
| Muscle Preservation | Yes | Concerns about muscle loss |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Research Level | Preclinical | Extensive human trials |
When to Choose 5-Amino-1MQ:
- Want to avoid appetite suppression/nausea
- Prefer oral administration
- Want to preserve muscle mass
- Have less aggressive weight loss goals
When to Choose Semaglutide:
- Need significant weight loss (>10%)
- Want FDA-approved option
- Can tolerate GI side effects
- Under medical supervision for obesity
5-Amino-1MQ vs AOD-9604
| Aspect | 5-Amino-1MQ | AOD-9604 |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | NNMT inhibition | HGH fragment (lipolysis) |
| Target | Cellular metabolism | Fat cells directly |
| Administration | Oral | Injection |
| IGF-1 Effect | None | None |
| Research Level | Preclinical | Phase 2 human trials |
| FDA Status | Research compound | GRAS status (food) |
Complementary Use: These two compounds work through different pathways and are sometimes stacked together.
5-Amino-1MQ vs HGH Fragment 176-191
| Aspect | 5-Amino-1MQ | HGH Frag 176-191 |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | NNMT inhibition | Lipolysis activation |
| Muscle Effect | Preserves | Minimal |
| Blood Sugar | May improve | Minimal effect |
| Administration | Oral | Injection |
| Anabolic | No | No |
5-Amino-1MQ vs Traditional Stimulants (Caffeine, Ephedrine)
| Aspect | 5-Amino-1MQ | Stimulants |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Metabolic enzyme inhibition | CNS stimulation |
| Heart Rate | No effect | Increases |
| Anxiety | No effect | Common |
| Sleep Disruption | Rare | Very common |
| Dependency | Not observed | Yes |
| Long-term Safety | Unknown | Concerning |
Comparison Summary
5-Amino-1MQ is best for:
- Those who want metabolic enhancement without appetite suppression
- People sensitive to stimulants or GLP-1 side effects
- Those seeking to preserve muscle during fat loss
- Users interested in anti-aging/NAD+ benefits
- Those preferring oral administration
5-Amino-1MQ may not be ideal for:
- Those needing dramatic weight loss quickly
- Anyone requiring FDA-approved treatments
- Those uncomfortable with limited human research
- People with contraindicated conditions
Stacking 5-Amino-1MQ
Many practitioners and users combine 5-Amino-1MQ with other compounds to enhance results through different mechanisms.
Popular Stacks
Stack 1: Comprehensive Fat Loss
- 5-Amino-1MQ (NNMT inhibition)
- AOD-9604 (lipolysis)
- Rationale: Multiple pathways for fat reduction
Stack 2: Metabolic + GH Optimization
- 5-Amino-1MQ (NNMT/NAD+)
- CJC-1295 + Ipamorelin (GH release)
- Rationale: Enhanced metabolism + growth hormone benefits
Stack 3: Anti-Aging Focus
- 5-Amino-1MQ (NAD+/SIRT1)
- NMN or NR (NAD+ precursors)
- Rationale: Multiple approaches to NAD+ optimization
Stack 4: Body Recomposition
- 5-Amino-1MQ (fat loss)
- BPC-157 (recovery/healing)
- Rationale: Fat loss while supporting tissue repair
Stacking Considerations
Benefits of Stacking:
- Target multiple mechanisms simultaneously
- Potentially enhanced results
- Synergistic effects
Cautions:
- More variables = harder to identify issues
- Increased cost
- No research on combined effects
- Should be approached conservatively
General Stacking Guidelines:
- Introduce one compound at a time
- Assess tolerance before adding more
- Start with lower doses when combining
- Monitor for adverse effects
- Work with a knowledgeable practitioner
Who Should Consider 5-Amino-1MQ
Ideal Candidates
May Benefit Most:
- Those with stubborn fat despite diet and exercise
- People who've plateaued on other approaches
- Those seeking metabolic optimization rather than appetite suppression
- Individuals sensitive to stimulants or GLP-1 side effects
- People interested in anti-aging and NAD+ optimization
- Those wanting to preserve muscle during fat loss
- Individuals with metabolic syndrome markers (insulin resistance, high triglycerides)
Who Should Avoid
Should NOT Use:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Those under 18 years old
- People with liver or kidney disease
- Anyone with active cancer (without oncologist approval)
- Those on medications without checking interactions
- Anyone seeking FDA-approved treatments only
- People uncomfortable with experimental compounds
Realistic Expectations
What to Expect:
- Gradual fat loss over 4-8 weeks
- Improved body composition (may not see dramatic scale changes)
- Potential increases in energy and focus
- Best results when combined with proper diet and exercise
What NOT to Expect:
- Dramatic overnight results
- Complete replacement for diet/exercise
- Appetite suppression effects
- Guaranteed results (individual variation exists)
Frequently Asked Questions
General Questions
Is 5-Amino-1MQ a peptide?
Technically, no. 5-Amino-1MQ is a small molecule compound, not a peptide (peptides are chains of amino acids). However, it's often discussed alongside peptides in metabolic and fat loss contexts because of similar applications.
Is 5-Amino-1MQ FDA approved?
No. 5-Amino-1MQ is not FDA approved for any use. It exists as a research compound. There are no published human clinical trials as of 2025.
Is 5-Amino-1MQ legal?
In most jurisdictions, 5-Amino-1MQ occupies a legal gray area. It's not a controlled substance but also not approved for human consumption. It can typically be sold as a "research chemical." Laws vary by country.
How long does it take to see results?
Most users report noticeable effects within 4-6 weeks. Some may notice energy improvements within 1-2 weeks. Full body composition changes typically develop over 6-12 weeks of consistent use.
Dosing Questions
What is the best 5-Amino-1MQ dosage?
Common protocols use 50mg taken 2-3 times daily with meals, for a total of 100-150mg daily. However, optimal human dosing hasn't been established through clinical trials. Start conservatively and adjust based on response.
Should I take 5-Amino-1MQ with food?
Yes, taking 5-Amino-1MQ with meals is generally recommended. This may improve absorption and reduce any potential GI discomfort.
Do I need to cycle 5-Amino-1MQ?
Yes, cycling is recommended. A typical protocol is 6-8 weeks on, followed by 2-4 weeks off. Effects may diminish with continuous use, and cycling helps maintain effectiveness.
Can I take 5-Amino-1MQ long-term?
Long-term safety in humans is unknown. Until more research is available, cycled use with regular breaks is advised. Work with a healthcare provider to monitor health markers.
Mechanism Questions
How does 5-Amino-1MQ work for fat loss?
5-Amino-1MQ inhibits the enzyme NNMT, which allows more NAD+ to be produced in cells. Higher NAD+ activates SIRT1 (longevity gene), which shifts metabolism toward fat burning instead of fat storage. Importantly, this happens without suppressing appetite.
Will 5-Amino-1MQ affect my hormones?
Based on current evidence, 5-Amino-1MQ does not appear to significantly affect testosterone, cortisol, or thyroid hormones. This is different from many other fat loss compounds.
Does 5-Amino-1MQ cause muscle loss?
No—in fact, it may help preserve muscle during fat loss. Unlike calorie restriction or GLP-1 agonists which can cause muscle loss, 5-Amino-1MQ appears to preferentially target fat tissue.
Safety Questions
What are the side effects of 5-Amino-1MQ?
Reported side effects are generally mild: occasional nausea, headache, drowsiness, or mild GI upset. No serious adverse effects have been reported in preclinical studies or clinical practice. However, human safety data is limited.
Can I take 5-Amino-1MQ with other medications?
Drug interactions haven't been formally studied. Consult with a healthcare provider before combining with any medications, especially those affecting metabolism, liver function, or blood sugar.
Is 5-Amino-1MQ safe for diabetics?
5-Amino-1MQ may actually improve insulin sensitivity based on animal research. However, diabetics should consult their doctor before use, especially if taking blood sugar medications, as levels may need monitoring.
Comparison Questions
Is 5-Amino-1MQ better than semaglutide?
They're different tools for different situations. Semaglutide is FDA-approved with proven efficacy (10-15% weight loss) but causes appetite suppression and often nausea. 5-Amino-1MQ works through metabolic enhancement without appetite effects but has less human research. Choice depends on individual needs and risk tolerance.
Can I stack 5-Amino-1MQ with other peptides?
Yes, 5-Amino-1MQ is commonly stacked with compounds like AOD-9604, GH peptides (CJC-1295/Ipamorelin), or healing peptides (BPC-157). Different mechanisms may provide synergistic effects, but introduce compounds one at a time to assess tolerance.
Scientific References
Primary Research
Neelakantan H, et al. (2018)
- "Selective and membrane-permeable small molecule inhibitors of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase reverse high fat diet-induced obesity in mice"
- Biochemical Pharmacology
- PMC5826726
Kraus D, et al. (2014)
- "Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase knockdown protects against diet-induced obesity"
- Nature
- nature13198
Neelakantan H, et al. (2022)
- "Reduced calorie diet combined with NNMT inhibition establishes a distinct microbiome in DIO mice"
- Scientific Reports
- PubMed 35013352
NNMT Research
Liu Y, et al. (2021)
- "Roles of Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes"
- BioMed Research International
- PMC8337113
Zhang J, et al. (2024)
- "Nicotinamide N-methyltransferase (NNMT): a novel therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome"
- Frontiers in Pharmacology
- fphar.2024.1410479
Babula P, et al. (2024)
- "Nicotinamide N‐methyltransferase inhibition mitigates obesity‐related metabolic dysfunction"
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
- Wiley Online Library
Ruf S, et al. (2018)
- "Genetic Nicotinamide N-Methyltransferase (Nnmt) Deficiency in Male Mice Improves Insulin Sensitivity in Diet-Induced Obesity"
- Diabetes
- ADA Journals
Clinical Information Resources
Conclusion
5-Amino-1MQ represents a novel approach to fat loss and metabolic optimization—one that works through NNMT inhibition rather than appetite suppression or hormonal manipulation. By enhancing NAD+ levels and activating SIRT1, it shifts the body toward fat burning while potentially preserving muscle mass.
Key Takeaways
Unique Mechanism: 5-Amino-1MQ inhibits NNMT enzyme, boosting NAD+ and activating metabolic pathways that favor fat oxidation over storage
No Appetite Suppression: Unlike GLP-1 agonists, 5-Amino-1MQ doesn't cause nausea or dramatically reduce appetite—weight loss comes from metabolic enhancement
Muscle Preservation: Research suggests fat loss occurs preferentially, without the muscle loss seen with many other interventions
Strong Preclinical Evidence: Animal studies show 35% reductions in fat mass with no adverse effects, but human clinical trials are lacking
Well-Tolerated: Side effects are generally mild (nausea, headache) when they occur
Cycling Recommended: Best used in 6-8 week cycles with breaks to maintain effectiveness
Complementary Benefits: NAD+ enhancement may provide anti-aging, energy, and cognitive benefits beyond fat loss
Research Compound Status: Not FDA-approved; human safety and efficacy data are limited
Who Should Consider It
5-Amino-1MQ may be appropriate for individuals seeking metabolic enhancement for fat loss who:
- Want to avoid appetite suppression side effects
- Are sensitive to stimulants
- Have plateaued on other approaches
- Are interested in anti-aging/NAD+ benefits
- Accept the limitations of research compound status
As with any experimental compound, working with a knowledgeable healthcare provider and monitoring health markers is essential. While the science behind NNMT inhibition is compelling, human clinical trials will ultimately determine whether 5-Amino-1MQ lives up to its preclinical promise.
Last Updated: December 2025
Disclaimer: This article is for educational and informational purposes only. 5-Amino-1MQ is not FDA-approved for human use. No human clinical trials have been published. The information provided does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare provider before using any research compounds. Individual results may vary.
Keywords: 5-amino-1mq, 5 amino 1mq, NNMT inhibitor, nicotinamide N-methyltransferase, fat loss peptide, NAD+ booster, SIRT1 activator, metabolic enhancement, weight loss compound, 5-amino-1mq dosage, 5-amino-1mq side effects, 5-amino-1mq benefits, 5-amino-1mq vs semaglutide


